-
Certification
ISO9001/ISO14001/IATF16949
ROHS/UL/REACH/FDA+86 13291521819
Welcome to be our distributor
Today, as electronic products continue to develop towards high reliability and integration, encapsulation has become an indispensable process in many electronic systems. Whether it is automotive electronics, power modules, industrial controls, or LED lighting, component encapsulation is widely used. But in practical engineering, some people still often ask: why do components need to be sealed? How to choose different types of sealant?
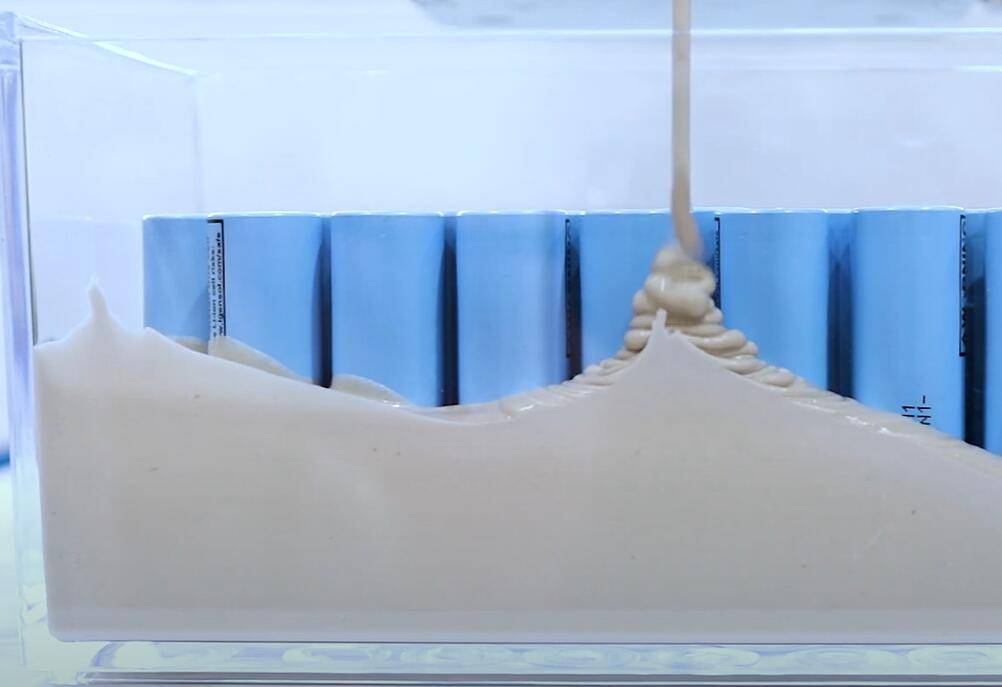
Understanding these two issues is an important prerequisite for doing a good job in the reliability design of electronic products.
Battery thermal conductive sealing adhesive
Battery thermal conductive sealing adhesive
Challenges faced by electronic components in real-world application environments
Components often operate stably under laboratory testing conditions, but in practical applications, they need to face long-term temperature changes, moisture intrusion, mechanical vibrations, and complex electrical stresses. High and low temperature cycling can cause thermal expansion and contraction of materials, and humid environments may lead to corrosion of solder joints and pins. Continuous vibration can accelerate solder joint fatigue. When these factors exist alone, their impact is limited, but in long-term operation, they often overlap and become the main cause of component failure.
Why do electronic components need to be sealed
The primary function of sealing is environmental protection. After curing, the sealing adhesive forms a continuous and dense protective layer, which can effectively block water vapor, dust, and chemical pollutants, preventing performance degradation caused by moisture and corrosion. This is particularly crucial in outdoor equipment, automotive electronics, and industrial sites.
Next is to enhance electrical safety. In high-voltage or high-frequency applications, the spacing between components continues to shrink, increasing the risk of creepage and discharge. Sealing adhesive has stable electrical insulation performance, which can fill gaps, evenly distribute electric fields, and improve the insulation reliability of the system.
Sealing can also reduce the risks caused by mechanical vibration and impact. During the operation or transportation of vehicles, equipment, or transportation, vibrations and impacts can cause repeated stress on solder joints. After curing, the sealing adhesive can fix the position of the components and absorb external stress through the toughness or elasticity of the material, reducing structural fatigue.
In addition, sealing is also of great significance for controlling thermal stress and improving lifespan. Components undergo repeated thermal cycles during power on and off processes, and the differences in thermal expansion coefficients of different materials can easily generate internal stresses at solder joints and packaging interfaces. Suitable sealant can release stress through low shrinkage or flexible structure, thereby extending its service life. In some power device applications, encapsulation materials also serve as auxiliary thermal conductors, helping to conduct heat more evenly.
How to choose different types of sealing adhesive
After clarifying why components need to be sealed, the selection of sealing adhesive becomes crucial. There are significant differences in performance characteristics and applicable scenarios among different types of potting adhesives.
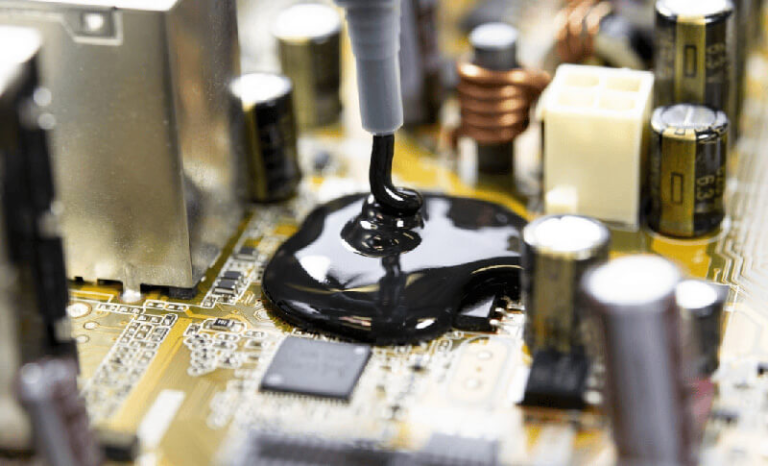
potting compound
Epoxy potting compound
It usually has high mechanical strength, good chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, suitable for applications with high structural fixation requirements and relatively stable working environments, such as some industrial electronics and power modules. However, epoxy materials are relatively rigid after curing and may generate high internal stresses in scenarios with significant temperature changes, which need to be fully evaluated during the design phase.
Filled PU Potting
It performs well in flexibility and stress buffering, effectively absorbs vibration and thermal deformation, and is suitable for applications that are sensitive to mechanical impact and thermal cycling. However, its high temperature resistance is usually not as good as epoxy and silicone, and careful selection is needed under long-term high temperature conditions.
Organic silicon sealant
Known for its wide temperature range, low stress, and excellent electrical insulation performance, it is particularly suitable for applications that require high reliability, such as automotive electronics, LED lighting, and long-term power systems. Its flexible structure helps to release thermal stress and is more friendly to components, but when selecting, it is also necessary to consider the adhesive requirements and cost factors comprehensively.
Overall, the reason why components need to be sealed is not determined by a single factor, but by the combined effects of environmental protection, electrical safety, mechanical reliability, and thermal management requirements. There is no fixed answer on how to choose different types of sealant. Only by combining specific application environments, working temperatures, stress conditions, and reliability goals can the truly suitable material be selected. Treating encapsulation as a part of system level design, rather than a simple post-processing process, is the key to improving the long-term reliability of electronic products.
Tags: Why do electronic components need to be sealed? Organic silicon sealing adhesive · Sealing process · How to choose sealing adhesive · Epoxy sealing adhesive · Electronic component sealing · Electronic sealing material · Polyurethane sealing adhesive
- Epoxy resin adhesive and industrial epoxy resin adhesive
- Silicone Gels VS Epoxy Resins: A Guide to Depth Comparison for Electronic Packaging Materials
- What is the difference between sealant and hot melt adhesive? Read the article to understand their respective advantages and application scenarios
- The multifunctionality of single component epoxy adhesives: applications, advantages, and key considerations
- What is the difference between sealant and hot melt adhesive? Understand clearly in one minute!
Tell us your request...
COPYRIGHT ◎ 2023 Elaplus Functional Materials Co. LTD

